How To Write Non-binary Characters: Part III.
How to Write Non-binary Characters: Part III.
Visit PART ONE: the basics.
Visit PART TWO: the nitty gritty.
PART THREE: common pitfalls and easy fixes.
Here we’ll cover some common situations where writing respectful non-binary characters can be trickier.
Writing Non-human Non-binary characters.
Non-human non-binary characters aren’t inherently disrespectful to non-binary people, but it can easily become negative representation when there are no non-binary humans present, because it implies that those with non-binary genders are less human (and usually more monstrous or more alien) than people with binary genders. You can read more about why this is a problem in this full analysis by Christine Prevas.
There’s a very simple solution to this though: Write some non-binary humans. (Or, in the least, make it explicitly clear that non-binary humans exist, and are just as valid in their identity as anyone else.)
Writing Non-binary Villains.
This situation is very similar to the non-binary non-humans, but instead of implying that non-binary people are less human, it implies they are less moral, abnormal, depraved, or insane. Villainous figures in history have often have their villainy connected to or blamed on their non-gender conforming traits. We don’t want to add to that clinging transphobic and homophobic belief with modern fiction.
As with non-binary non-humans, having non-villainous non-binary characters can go a long way in offsetting this, as well as not connecting (or letting characters within the world connnect) the villain’s non-binary aspects with their perceived villainy. Instead of writing a non-binary villain, write a villain who also happens to be non-binary.
(On this note, I would be very cautious about writing villains who are being villainous because they’ve suffered from transphobia.)
Killing (your only) Non-binary Character.
This falls into the same category as the previous two sections, but it has just one solution: don’t kill your story’s only non-binary or trans character. Just don’t do it. If that character has to die to make the plot continue, let there be another primary non-binary or trans character in the story somewhere.
Writing “Coming Out” Scenes for Non-binary Characters.
Let’s break this into two different types of coming out:
Lees verder
More Posts from Yourwriters and Others
Hi! I’m trying to start a new story and I was wondering how would you build a new character from scratch? Like how would you go about creating them?
There are many different ways a character is conceived. You’ll need one of these things to start with:
name—you heard one that sounded cool to you, either the meaning, the pronunciation, or the ideas it brings to mind when you hear it.
look—you saw or imagined a character with certain physical features or garb, someone new and interesting that you want to know more about.
profession—you’re interested in exploring a certain occupation within a fictional setting and what kind of things might happen during the work day.
lifestyle—this can include profession, but it’s more about who they are (or who they pretend to be) at all hours of the day/night.
archetype—you want to explore a character who is the sidekick, villain, mentor, or some other archetype within a story.
From there you shape them into a three-dimensional person with these aspects (which in themselves can inspire a new character):
family/friends—the people who raised, supported, and cared for them (or didn’t) at different points in their lives and thus affected their personality.
culture—the lifestyle of the community they identify with which can include shared customs, traditions, beliefs, foods, entertainment, etc.
skills—stuff they’re good at, but also stuff they’re bad at because both are important for you to know.
backstory—the combination of big experiences that shaped them permanently and that they might think about on a regular basis; a loved one dying, a successful career, a big mistake, and/or a long-term illness.
experiences—individual events that shaped who they are now, but aren’t really a big part of their life story; that time they had their first kiss, played their first sport, encountered a wild animal, and/or learned to cook their own meal.
traits—inherent aspects of their personality that can be their strengths and weaknesses depending on how they improve on or neglect them; they are very kind and compassionate, but easy to take advantage of and are sometimes overly fussy.
beliefs—their driving force, their purpose in life, the reason they get up in the morning and continue to exist.
personality—the combination of skills, beliefs, and cultural norms that make them an individual based on their experiences and upbringing, as well as inherent traits.
Now, the reader does not want to know all this stuff on the first page. In fact, the reader might not need to know much of it at all. You do, and what you include in your story should be primarily stuff the reader needs to know with just a sprinkling of other character information. Some books might give the MC’s entire biography in the first chapter, but even Charles Dickens knew to save the best details for later.
These bullet points work for all characters, not just your main protagonist(s). A writer doesn’t need to know every detail about every side character, but it helps to think of each one as a whole person. Makes the writing feel more authentic.
+ If you benefit from my updates and replies, please consider sending a little thank you and Buy Me A Coffee!
+ HEY, Writers! other social media: Wattpad - AO3 - Pinterest - Goodreads
So You Want To Write A Book..
Where Do Writers Find Their Ideas?
On Inspiration
How To Write A Novel
Getting Started With A Book
Hints About Writing A Story
Novel Outlining 101
From Notes To Novel
Plotting A Novel
Why Don’t I Have A Plot, And Where Do I Get One?
How To Create A Character
Creating Characters
Character Creation
Name That Character! (2)
You And Your Characters
How To Write Backstory Without Putting Your Reader To Sleep
How To Use Foreshadowing
How To Write Dialogue (2)
How To Make Your Writing More Interesting
Writing Block
How To Get Unstuck
Advice For Young Writers (2)
On Word Counts And Novel Length
Top 4 Ways to Know Your Idea is Novel-Worthy
How A Book Gets Published
How Do You Go About Getting Published
And remember: Google is your best friend.
I love that excerpt!

cocaine, a car wreck, and an apple pie recipe.
a modern retelling of sophocles’ ajax, wintersong is 18-year-old and terribly wayward hollis knox’s aching love letter to all the good in the world: grocery store aisles’ uneven green-and-white flecked tiles, shared secrets behind calloused hands, and little brothers’ sunday morning swim meets. all the good that atrophies too fast.
goal words: 50,000
current words: 21,000
weheartit board
here’s an excerpt from the first chapter:

let me know what you think!
p.s. i follow from studylikeathena.
PREPPING YOUR NOVEL.
if you want to start your novel but you’re not sure where to start, i’ve collected a bunch of resources to help you along! this includes characterization, plotting, worldbuilding, etc. @made-of-sunlight-moonlight
CHARACTERS.
name generator: this one is pretty handy. it has a bunch of different generators based on language, gods, fantasy, medieval, archetypes, etc.
➥ reedsy name generator
personality types: this is just the standard mbti personality list. it lists the strengths and weaknesses of each type, as well as how they do in relationships, etc.
➥ mbti 16 personalities
enneagram: the enneagram personality types. this may help with characterization because it has “levels of development.” it also lists common fears, desires, and how each type interacts with one another.
➥ enneagram types
emotional wound: your character should have something they believe about themselves that isn’t true. (ex: i’m worthless, i’m powerless.) this should start with an “origin” scene from their past, where something happens to create the wound. then there are three “crossroads” scenes to brainstorm, where things could have gone right for your character, but didn’t due to the wound, and because of that strengthened their belief in the wound. this helps you figure out why your character acts like they do. this is a really important one!!!
➥ emotional wound explained
WORLDBUILDING.
worldbuilding template: this is a pretty good template / guide about how to build your world. it talks about geography, people, civilizations, magic, technology, economy, and politics. (you have to download this through email though.)
➥ reedsy worldbuilding template
world anvil: if you really really want to go in-depth — this website is for you. there is so much you can do with this; i can’t list it all. history, timelines, important objects, cities, species — you name it, it’s probably on there.
➥ world anvil website
worldbuilding bible: this is just a general list on things to think about when worldbuilding.
➥ ellen brock’s worldbuilding bible
world creator: this website generates an entire planet. you can play around with the amount of land, as well as climate, although i’m not sure since i haven’t used it too much. here is the link if needed, though!
➥ donjin fractal world generator
inkarnate: this is a really commonly used one. it’s free and makes good quality maps. you can lay out cities, landmarks, regions, and they even have little dragon drawings you can put on your map.
➥ inkarnate website
a tip: don’t over-worldbuild! you’ll end up spending a lot of time on things you won’t need. focus mainly on the things that you will use!
PLOT.
plot generator: this one’s kind of nice because you can lock elements of the plot that you like. that way you can get rid of the ones you don’t like while keeping the ones you do.
➥ reedsy plot generator
writing exercises: this one has a couple different generators, including one that gives you a situation, characters, and themes.
➥ writing exercises
plot cheat sheet: this lists a whole bunch of plotting methods and their basic steps. i would play around with them and see which one works best for your method.
➥ plot cheat sheet by ea deverell
plot formula: this is mentioned on the cheat sheet, but it lists a bunch of beats and scenes which you might want to consider for those beats. kind of fill-in-the-blank-ish sort of thing?
➥ plot formula by ea deverell
save the cat: a method of plotting also on the plot cheat sheet above, but i wanted to point it out. i have been using this recently by taking a giant piece of paper, laying it out onto the floor, and making a timeline. pivotal scenes go on the right (ex: catalyst), while the bulk of scenes go on the left (ex: fun and games). i didn’t really have a website on this, but here is one that explains the beats. (i might make a post about this later, though?)
➥ save the cat explained
ETC.
story planner: this basically has a lot of templates that cover everything up there. the problem is that you get a free trial for a little while where you get as many documents as you want, then you have to pay for it. (although you can get around this by copying and pasting into a doc...?)
➥ story planner website
describing / related words: these kind of go hand in hand. if you put a word intothese websites, they will give you either a list of related words or adjectives respectively.
➥ describing words website
➥ related words website
ea deverell: i've pulled a lot of stuff from this website to put in this post, but there's a lot more that can be used. Like a lot on basically anything — plot, character, world, outlining, writing itself.
➥ ea deverell website
reedsy: again, i've pulled a lot of stuff from them to put in this post, but there's much more. it's similar to the ea deverell one.
➥ reedsy website
canva: this is more for making aesthetics and covers. (this thing is really helpful —and free!) although if you use this, i'd suggest pulling pictures off a website like unsplash; that way the pictures are free to use.
➥ canva website
i hope you found this helpful!! :) happy writing!!
Tips on Writing a Great Short Story

Weeks ago I was asked to do an article on short stories, specifically. What makes a short story great? And how is it different from writing a novel?
To be honest, writing a novel and writing a short story are very similar in many ways, and most of the techniques I’ve written about on my blog apply: creating complex characters, writing great dialogue, utilizing subtext, including hooks . . .
Sure, there are some exceptions, as always. You can find famous short stories that don’t really have complex characters, for example, but often such stories are really short stories–maybe by today’s standard, considered flash fiction. Here is a famous flash fiction story:
For sale: baby shoes, never worn
Does that really tell us much about the complexity of the characters? Not really. But it does still have great subtext.
So keep in mind that there are always exceptions when it comes to writing, but they are just that, exceptions.
So let’s got started.
Focus

One of the most important things about writing a short story is to keep it focused. Technically, novels should be focused too, but their focus has a broader range whereas short stories need to be narrower, like a flashlight beam compared to a laser beam. A common problem I’ve seen with newer writers is that they try to fit a novel-length concept into 50 pages. Problematic. Here are some ways to avoid that.
Limit Plotlines–In a novel, you will need a lot of plotlines to carry the story; if you don’t have that, a novel will start to feel repetitious since it lacks variety for so many pages. But in a short story, you need to limit your plotlines. Many short stories really have one plotline, with two components working closely together: the outer journey and the inner journey. Think about the premise or main concept of your short story, and keep a laser-beam focus on that. Aim to go deep into the concept, not broad on the topic.
Limit Your Characters–In a short story, you’ll usually focus largely on one main character and that character’s arc. The more focal characters you include, the more length you typically add. Sure, you can write a story with more than one focal character–you might be able to get away with maybe two. If you have more than that though, usually the focal characters–while individuals–have the same goals and function as a unit. As opposed to most novels, where each focal (or viewpoint) character may have somewhat different goals and more of their own, individualized journeys. (Again, keep in mind that everything in this post is generally speaking).
A good word of advice that gets pushed around in the industry, related to character and plot, is that in a short story, you should specifically write about the most important event that happened in that character’s life. I don’t know that I agree with this 100%, but it’s a good thing to keep in mind when evaluating plot and character. Capture the most important event, which naturally means that it will be an event that changed the character.
Laser-Beam the Theme–Unfortunately, people still talk and treat theme like it’s this elusive animal–something wild and beautiful, but dangerous if caged. In reality, the more you understand about theme, the more intentional you can be about it. It’s only dangerous when you try to tame it improperly, because you don’t understand it. For a recap on how theme actually works, check out this post, “How to Write Your Story’s Theme”
Themes are fantastic for focusing stories (and especially in short stories that may seem to lack a feeling of … cohesion). And because a lot of people don’t understand how to do them, you can really stand out if you master the theme in your story. Theme is what makes a story feel timeless. It sticks with us after we are done, so we aren’t left closing the book and thinking, Well that was entertaining, time to get back to normal life! If you read five excellent stories, but only one of them has a powerful theme that changed you, guess which one you will think about long, long after you’ve finished it?
In a novel, you have room to explore a theme topic rather broadly. Consider all the ways the theme topics of mercy and justice are illustrated and explored in Les Mis. In a novel, you can also explore how the theme topic interacts with other theme topics, societies, and ideologies. In a short story, you are going to be more laser-focused. Take the classic fable of The Tortoise and The Hare–it stays laser-focused on really one illustration of the theme. It doesn’t go into, say how in some situations in the real world, getting a head start can have benefits. So focus in on a particular rendition or two (but probably no more than three) of your thematic statement.
Often the most famous and powerful short stories are so great because they say something profound in a small amount of space. In a way, it’s similar to poetry. Professional poetry isn’t actually about using beautiful words (which is what a lot of people who have never legit studied it seem to think)–it’s about capturing specific, significant ideas, concepts, and images, in a brief space, for maximum impact. Great short stories function in similar ways, except you have more room to develop a powerful thematic thread. It can be hard to impact a reader in such a short space with the characters and plot, but you can really hit them in the feels with the theme.
Keep reading
hi I'm 22 but I want to write a story about people in their forties. Essentially the point is that people are still figuring themselves out at any age. Do you have any advice for writing about an age group so different from yours? Especially for me, who has not experienced their forties yet, whereas older adults writing YA have experienced that time in their lives. thanks
Writing an Age Group You Have No First-Hand Experience Of
Hi! First, I would do some research. Movies, books, TV shows, articles, and interviews that center around the age group. While the emotions and trials they are going through is a universal thing, their actual issues are usually specific to that age group.
For forties, I would watch The Meyerowitz Stories (Netflix) and read the play or watch the movie August: Osage County. These focus on the common trials of forty-year-olds such as aging/dying parents, divorce, teenage kids, reconciling with estranged family, success past 30, and the likes.
Second, remember that everyone is at a different place than others their age. The forties, especially, have a lot of diversity in living situations. Some are getting a divorce or remarrying and some are just getting married or will never marry. Some are sending kids off to college and some are just starting a family. Some are going back to school or working an entry-level job and some are working their dream job. Some are well-off and some are in massive debt. Some feel old and some are in their prime.
Third, find a common struggle or fear within the age group. For people in their twenties, it’s usually choosing the right path. By forty, it’s usually worrying if they chose the right path and if it’s too late to change.
And fourth, get in the headspace through backstory. How many experiences they’ve had is just as important as the kind of experiences and vice versa. Figure out the life they have fit into all those years.
Hope this helps!
Never mow the same grass twice — How to improve faster as a writer
One of the most important writing lessons I ever learned came, surprisingly, from my college trumpet instructor.
“Michael,” he’d say with a heavy sigh, pulling off his glasses and rubbing the lenses with the bottom of his shirt. “You know I hate to mow the same grass twice.”
It was a phrase he used a lot, in band and private lessons, whenever someone made a mistake he’d already told them to correct. Because in his mind, once he’d identified a mistake in your performance, you needed to do everything you could to keep it from happening again, for two reasons.
First, because as he said, he doesn’t like to mow the same grass twice. And second (and more importantly), because if you let yourself repeat a mistake, that mistake will start to become a habit.
A bad habit.
And the more you let yourself repeat that habit, the more deeply ingrained it becomes, making it increasingly difficult to fix and slowing your progress as a musician (or artist, or writer). So his suggestion was this: Identify what needs to change, and firmly commit to fixing it now.
Confession Time
So. I was a very average trumpet player. My instructor and I had a great rapport, but he had to tell me to mow the same grass twice, three times, and more often than he ever would have liked, because I just wasn’t focused or passionate enough about trumpet to fully commit to his advice.
But I was focused and passionate enough about fiction to commit to his advice when it came to writing. So I applied his mindset in my creative writing workshops, particularly when I started my MFA.
And I tell you what, everybody. It worked wonders — helping me improve enough in that first year alone to win our MFA program’s top fiction prize and to earn a teaching assistantship.
3 Steps to Quickly Improve Your Writing
With my trumpet instructor’s advice in mind, I put a 3-step process on loop throughout my time in the MFA:
Share a short story with your fellow writers. (A workshop is great, but online writing friends work too.)
Sift through everyone’s feedback to find one high-priority “bad habit” in your writing that they seem to be honing in on.
When you sit down to write your next story, commit to breaking that habit at any cost, even if it means making other mistakes because of it. (New mistakes are better than old mistakes.)
This is How it Went for Me
The first short story I shared in my MFA workshop had a clear issue: the narrator was passive and underdeveloped. One of my classmates called him a “window character,” someone through whom we could observe the other, more interesting characters who actually drove the plot. The rest of the workshop agreed, and looking back at some of my past stories, I realized that passive narrators had become a deeply ingrained habit of mine.
So the next time I wrote a story, I strictly committed myself to writing a more active narrator.
The Result?
A moderately active narrator. Not perfect, but better than I’d done in a long time. It was progress — me chipping away at the bad habit.
The next story I wrote showed much more progress. It had a highly active narrator, and so did the story after that. And that’s when a new, better habit formed: writing active narrators without even thinking about it. And that let me shift my focus to improve upon something else (such as making all my narrator’s actions stem from their core emotional struggle). And something new again after that (using more figurative language, loosening up my writing voice, etc.).
And that’s how you can improve, too. The goal, again, is to use peer feedback to identify habits in your writing you don’t like, and then to mentally commit to replacing them with habits you want, one by one.
It’s a slightly different way to approach feedback. We tend to primarily use feedback as a way to help us improve an individual story — but it’s also a fantastic opportunity to improve your future first drafts.
You’ll be surprised how quickly your writing improves when you do this.
The key, though, is to commit to tackling just one major habit at a time. Why? Because writing is hard, friends, and fiction is a complex tapestry of various techniques, all coming together at once. That means your attention is always inevitably split while writing, so if you try to fix multiple habits at once, you’ll likely spread your attention too thin to succeed.
So identify a single change you want to see in you writing. Make it happen the next time you write a story, no matter what. Then, before you sit down again to write the next story, find something new you want to change or improve.
You’ll love what happens to your writing when you commit to never mowing the same grass twice.
And when you do, far away, in a brightly-lit college band room in Minnesota, my old instructor will raise a hand to conduct a trumpet ensemble, pause — and smile.
— — —
For writing advice and tips on crafting theme, meaning, and character-driven plots, check out the rest of my blog.
And if you’re feeling discouraged, remember this: Every story has something wonderful inside it, including your own.
Hey! Do you have any tips for people who've reached a block in their writing? I've been trying to plan out a plot for my book, but I've reached a point where I can't think of anything else
What to Do If You Get Stuck While Outlining Your Plot
Hi! Thanks for writing. Getting blocked can happen at all stages: Before writing, during writing, during outlining, in the idea stage, etc. But since you specifically said you’re reaching a block in your plot planning, I’ll address that :)
#1 Make sure your character’s motivation & conflict are “big” enough
If your character doesn’t have a book-length problem, you can get stuck trying to fill in empty space in the plot. In order to find more events to flesh out your story, you may need to make adjustments. Is their desire strong enough to fuel a book? Is the conflict big enough? Is their problem difficult to solve? If not, how can you make their problem harder? Or take longer to resolve?
You might need a combination of a fiercer desire, a bigger problem, more problems, more obstacles, and/ or a more stubborn antagonist to reveal potential scenes and events. For help with your character’s motivation and conflict, check out the PDF “Creating Character Arcs” in my Free Resource Library.
#2 Plot your story backwards
This can help you make sure you have a strong enough ending and open up new possibilities you might not have noticed while plotting forward. I have a post about it here.
#3 Use the but/therefore method
The but/therefore method is a great way to fill holes. It tests the cause-effect connections between your plot and character and almost always reveals gaps that need to be addressed with new or stronger scenes. Use this template for each scene or chapter:
Main character wants ______, but _______, therefore ______.
What comes after “wants” is the motivation for that chapter or scene. After “but” goes the conflict or obstacle. After “therefore” is the result or action the character takes, which leads into the next goal, and so on, and so on.
Chapter-by-chapter it might look something like this:
Chapter 1: Julian wants to ask Matt to the dance, but he’s scared of being rejected, therefore he slips a cryptic note into Matt’s locker.
Chapter 2: Matt doesn’t see the note. Now Julian wants to get into his locker and retrieve it, but the principal sees him trying to jimmy open the lock, therefore Julian is given detention for a week.
You can also do this scene-by-scene. My suggestion would be to start with the chapter outline, see what it reveals, then move into the scenes if you still feel stuck.
#4 Ask questions
Classic un-sticking questions start with “what if” or “why”? Asking questions can unlock new story directions you might not have noticed were there before.
What if the main character’s ex-boyfriend came back to town? What if they didn’t achieve that small goal back in chapter 4? What if they were hiding something? etc.
Why are they avoiding their sister? Why is it so difficult for them to apologize? Why haven’t they quit their job if they hate it so much? etc.
#5 Consider creating a subplot (or two or three)
A book-length story usually needs a few side stories to flesh out the main one. Look for areas of your story that could be expanded, characters that might take the story down a related tangent, and conflicts that seem small but could be bigger with some digging.
#6 Take a break
Sometimes, you just need to give it a rest. Walk away from your outline for at least a week. When you come back, you may see things you didn’t see before and be able to breathe new life into it. In the meantime, let your mind wander. It’s amazing what creative solutions writers can come up with when they aren’t “trying.”
//////////////
The Literary Architect is a writing advice blog run by me, Bucket Siler. For more writing help, check out my Free Resource Library, peruse my post guide, or hire me to edit your novel or short story. xoxo
I was wondering if you knew any basic guides to outlining a novel for the first time?
Outlining a story is very, very important. Without an outline and thorough planning, your story will veer off in wildly different directions and will cost you a ton of time editing later, like my book did.
1. Get the characters down first
Characters are like the chess pieces of the story. Their moves and strengths/weaknesses will decide what is going to happen and how it will happen. Sure, you can have a nice plot and setting, but without the characters, the story is meaningless.
Here is the character chart that I usually use:
Name (First/Middle/Last/Maiden name)
Aliases/Nicknames
Age
Race
Gender
Sexuality
Height
Weight
Eye color
Hair color
Clothing style
Religion
Political views
Personality Traits
Strengths and Weaknesses
Likes and Dislikes
Family
Friends
Enemies
Role in the story
Backstory/past
2. Choose a template
Just bulleting the events does not give the plot the dimension that it deserves and does not really accommodate side plots.
I personally use the zigzag method that I discovered from this post. I branch off of the zigzags for my side plots so it looks kind of like a graph.

You can also use the subway method, which I found on the nanowrimo website.
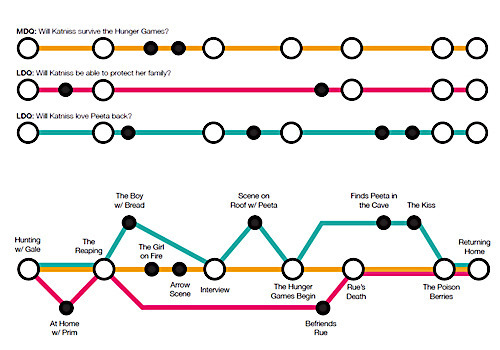
There are a whole other host of outlines to choose from if you search them up!
3. Know that you don’t have to stick to it
An outline is just that: an outline. It’s not the final decision for the plot, it’s the first draft for the plot. If you’re writing and one of the points just isn’t working anymore, you don’t have to keep it because it was a part of your outline.
Write what feels right.
Happy outlining, and good luck with your story!
The Easiest Way to Name a Character
Nameberry.com
I have to mini-rant about this website. It’s a baby-naming site, but it is one of the best out there for authors– and I’m about to tell you why.
It’s a beautiful and organized site. And there are three main things that I love about it.
1. They have a list for everything.
Whether site-made or user-made, the list categories can range from basic to specific. Here’s a few examples: Baby Names with Animal Meanings, Biblical Place Names, Celestial Baby Names, One Syllable Baby Names, Classic Baby Names with a Twist. It’s good for when you know the country of origin of the character, you want them to have a certain tone right away, you want religious symbology, or you want something simple– whatever it is, if you have a general idea for a name, Nameberry has lists that have you covered.

2. They have THE best search engine!
For this, click on “Find A Name” in the right top corner below the search bar.

As you can see, you can get really specific. You don’t have to fill out all the boxes, so if you just want to see all names of Italian origin or all names that start with “X”, you totally can! This is especially helpful to writers with the “meaning” section. Add in that easter egg symbology!
They also have something called the Namehunter, where you put in names you like to bring up similar ones.
3. They are really in-depth with background on a name
This includes (usually): > the meaning > the origin > Commentary from “experts” (sometimes this section is BS, I ignore it.) > Famous people with that name > Pop Culture references with that name (which can include literature) > Nicknames and Variations > Variations from different languages/regions > Similar names > Popularity over the years

Trust me, if you’ve never used this website before– just try it! I love it so much, it’s so helpful. Easier than scrounging through a hundred websites for names that mean “earth” or “savior” and are also of Armenian origin.
-
 antihell liked this · 1 month ago
antihell liked this · 1 month ago -
 lizzie-wizard liked this · 1 month ago
lizzie-wizard liked this · 1 month ago -
 joselintoftlund liked this · 2 months ago
joselintoftlund liked this · 2 months ago -
 coolcakebaker35 liked this · 3 months ago
coolcakebaker35 liked this · 3 months ago -
 det-cupcake liked this · 7 months ago
det-cupcake liked this · 7 months ago -
 yuereadingaccount liked this · 10 months ago
yuereadingaccount liked this · 10 months ago -
 doesthevoidstareback reblogged this · 11 months ago
doesthevoidstareback reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 doesthevoidstareback liked this · 11 months ago
doesthevoidstareback liked this · 11 months ago -
 lastsun-blog2 liked this · 1 year ago
lastsun-blog2 liked this · 1 year ago -
 afloatingjay liked this · 1 year ago
afloatingjay liked this · 1 year ago -
 hydrangeahelper reblogged this · 1 year ago
hydrangeahelper reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 write-101 reblogged this · 1 year ago
write-101 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 aaapril0987 liked this · 1 year ago
aaapril0987 liked this · 1 year ago -
 heckcareoxytwit liked this · 2 years ago
heckcareoxytwit liked this · 2 years ago -
 gogogoat495 liked this · 2 years ago
gogogoat495 liked this · 2 years ago -
 cremebrulee-69 liked this · 2 years ago
cremebrulee-69 liked this · 2 years ago -
 franvkie liked this · 2 years ago
franvkie liked this · 2 years ago -
 nausicaaaaaa liked this · 2 years ago
nausicaaaaaa liked this · 2 years ago -
 deer-in-headlights-stare liked this · 2 years ago
deer-in-headlights-stare liked this · 2 years ago -
 cabin6halfblood reblogged this · 3 years ago
cabin6halfblood reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ridethemilkywaves reblogged this · 3 years ago
ridethemilkywaves reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 thegreatyin liked this · 3 years ago
thegreatyin liked this · 3 years ago -
 aco-mist reblogged this · 3 years ago
aco-mist reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 aco-mist liked this · 3 years ago
aco-mist liked this · 3 years ago -
 ghoulhistorian reblogged this · 3 years ago
ghoulhistorian reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 crustysquidward liked this · 3 years ago
crustysquidward liked this · 3 years ago -
 halfbloodliz liked this · 3 years ago
halfbloodliz liked this · 3 years ago -
 sunniekitty liked this · 4 years ago
sunniekitty liked this · 4 years ago -
 crimsonhawkmoth liked this · 4 years ago
crimsonhawkmoth liked this · 4 years ago -
 astar-illustrations liked this · 4 years ago
astar-illustrations liked this · 4 years ago -
 gray2424 liked this · 4 years ago
gray2424 liked this · 4 years ago -
 itsaglitchthing liked this · 4 years ago
itsaglitchthing liked this · 4 years ago -
 nothing-here-to-look-at liked this · 4 years ago
nothing-here-to-look-at liked this · 4 years ago -
 maduh-rr liked this · 4 years ago
maduh-rr liked this · 4 years ago -
 thegoatfiles liked this · 4 years ago
thegoatfiles liked this · 4 years ago -
 deflatedball liked this · 4 years ago
deflatedball liked this · 4 years ago -
 siffrinskicks liked this · 4 years ago
siffrinskicks liked this · 4 years ago -
 siffrinskicks reblogged this · 4 years ago
siffrinskicks reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 roxaro reblogged this · 4 years ago
roxaro reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 mazuru7 reblogged this · 4 years ago
mazuru7 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 roxaro liked this · 4 years ago
roxaro liked this · 4 years ago
