Latest Posts by chbnb - Page 2
From above the Blue Whale almost looks like a submarine...........
teunvanderzalm
Dive into the cosmos with the beautiful and ethereal voice of Lisa Gerrard! This song called Elegy is from her solo album Immortal Memory.

Strawberry Summer Moon

Cone and Foxfur Nebulae

The Gamma Cygni Nebula Image Credit: Min Xie, Chen Wu, Yizhou Zhang, and Benchu Tang
Sunset From The International Space Station
2022 May 29
Simulation TNG50: A Galaxy Cluster Forms Video Credit: IllustrisTNG Project; Visualization: Dylan Nelson (Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics) et al. Music: Symphony No. 5 (Ludwig van Beethoven), via YouTube Audio Library
Explanation: How do clusters of galaxies form? Since our universe moves too slowly to watch, faster-moving computer simulations are created to help find out. A recent effort is TNG50 from IllustrisTNG, an upgrade of the famous Illustris Simulation. The first part of the featured video tracks cosmic gas (mostly hydrogen) as it evolves into galaxies and galaxy clusters from the early universe to today, with brighter colors marking faster moving gas. As the universe matures, gas falls into gravitational wells, galaxies forms, galaxies spin, galaxies collide and merge, all while black holes form in galaxy centers and expel surrounding gas at high speeds. The second half of the video switches to tracking stars, showing a galaxy cluster coming together complete with tidal tails and stellar streams. The outflow from black holes in TNG50 is surprisingly complex and details are being compared with our real universe. Studying how gas coalesced in the early universe helps humanity better understand how our Earth, Sun, and Solar System originally formed.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap220529.html

NGC 2170, Stardust Angel
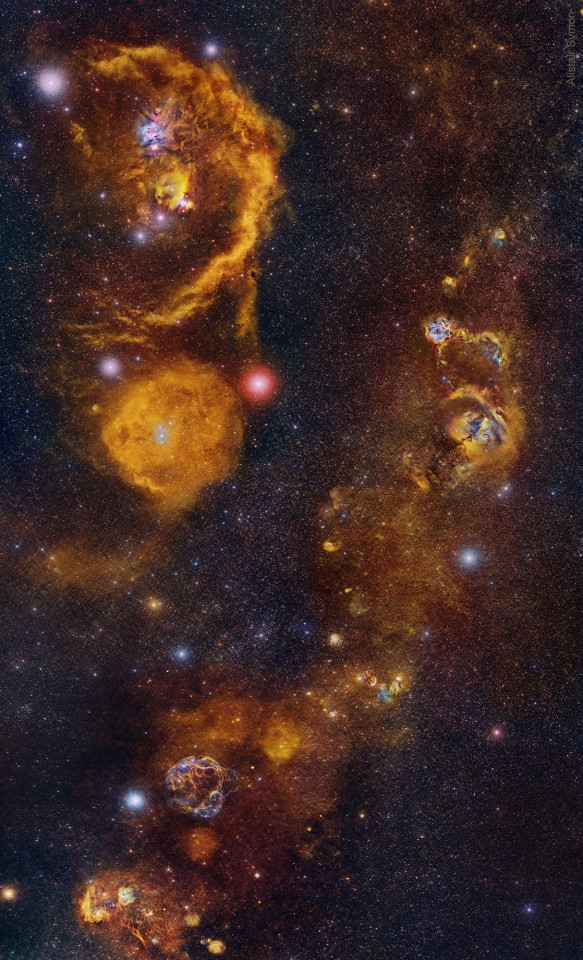

From Auriga to Orion

The Great Carina Nebula

Corona Australis

World’s Greatest Physicists, Geniuses Meet in 1927
Solvay Conference 1927
First row: Irving Langmuir, Max Planck, Marie Curie, Hendrik Lorentz, Albert Einstein, Pierre Langevin, Charles Eugene Guye, C. T. R. Wilson, Owen W. Richardson
Second row: Peter Debye, Martin Knudson, W. Lawrence Bragg, Hans Kramer, Paul Dirac, Arthur Compton, Louis de Broglie, Max Born, Niels Bohr
Third row: Auguste Piccard, Émile Henriot, Paul Ehrenfest, Edouard Herzen, Théophile de Donder, Erwin Schrodinger, Jules-Emile Vershaffelt, Wolfgang Pauli, Werner Heisenberg, Ralph Howard Fowler, Leon Brillouin
Absents: Sir W. H. Bragg, H. Delandres et E. Van Aubel
Image credit: Hadi Nur
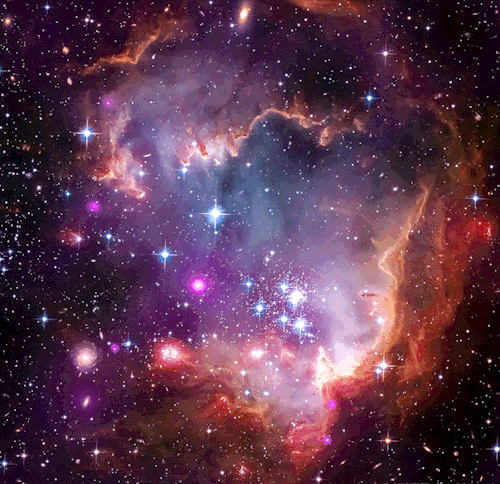
star cluster NGC 602 in the wing of the Small Magellanic Cloud

Orion, The Hunter

The Full Moon of 2021 via NASA https://ift.tt/3FWxNTm
Every Full Moon of 2021 shines in this year-spanning astrophoto project, a composite portrait of the familiar lunar nearside at each brightest lunar phase. Arranged by moonth, the year progresses in stripes beginning at the top. Taken with the same camera and lens the stripes are from Full Moon images all combined at the same pixel scale. The stripes still looked mismatched, but they show that the Full Moon’s angular size changes throughout the year depending on its distance from Kolkata, India, planet Earth. The calendar month, a full moon name, distance in kilometers, and angular size is indicated for each stripe. Angular size is given in minutes of arc corresponding to 1/60th of a degree. The largest Full Moon is near a perigee or closest approach in May. The smallest is near an apogee, the most distant Full Moon in December. Of course the full moons of May and November also slid into Earth’s shadow during 2021’s two lunar eclipses.
(Published January 01, 2022)

The James Webb Space Telescope lifted off on an Ariane 5 rocket from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana, at 13:20 CET on 25 December on its exciting mission to unlock the secrets of the Universe.
ESA/CNES/Arianespace




This is our home in the universe
Via Thomas Pesquet For European Space Agency
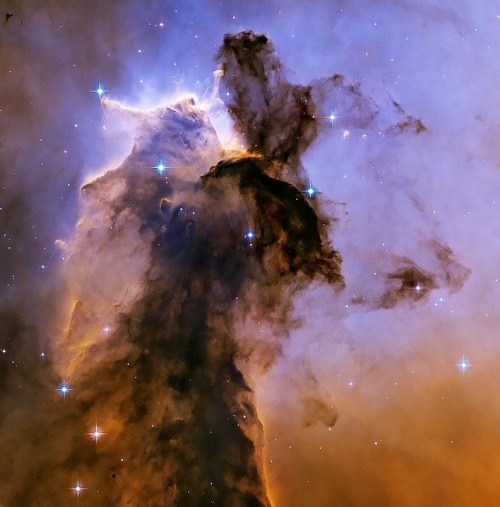


The Eagle has risen: stellar spire of gas & dust


Jupiter

NGC 6357, Cathedral of the Stars
whale breaks off
by Slater Moore



Spent the last week diving head first into Solar imaging
by Curt Morgan
How the Sun Affects Asteroids in Our Neighborhood
It’s no secret the Sun affects us here on Earth in countless ways, from causing sunburns to helping our houseplants thrive. The Sun affects other objects in space, too, like asteroids! It can keep them in place. It can move them. And it can even shape them.

Asteroids embody the story of our solar system’s beginning. Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids, which orbit the Sun on the same path as the gas giant, are no exception. The Trojans are thought to be left over from the objects that eventually formed our planets, and studying them might offer clues about how the solar system came to be.
Over the next 12 years, NASA’s Lucy mission will visit eight asteroids—including seven Trojans— to help answer big questions about planet formation and the origins of our solar system. It will take the spacecraft about 3.5 years to reach its first destination.
How does the Sun affect what Lucy might find?
Place in Space

Credits: Astronomical Institute of CAS/Petr Scheirich
The Sun makes up 99.8% of the solar system’s mass and exerts a strong gravitational force as a result. In the case of the Trojan asteroids that Lucy will visit, their very location in space is dictated in part by the Sun’s gravity. They are clustered at two Lagrange points. These are locations where the gravitational forces of two massive objects—in this case the Sun and Jupiter—are balanced in such a way that smaller objects (like asteroids or satellites) stay put relative to the larger bodies. The Trojans lead and follow Jupiter in its orbit by 60° at Lagrange points L4 and L5.
Pushing Asteroids Around (with Light!)

The Sun can move and spin asteroids with light! Like many objects in space, asteroids rotate. At any given moment, the Sun-facing side of an asteroid absorbs sunlight while the dark side sheds energy as heat. When the heat escapes, it creates an infinitesimal amount of thrust, pushing the asteroid ever so slightly and altering its rotational rate. The Trojans are farther from the Sun than other asteroids we’ve studied before, and it remains to be seen how sunlight affects their movement.
Cracking the Surface (Also with Light!)

The Sun can break asteroids, too. Rocks expand as they warm and contract when they cool. This repeated fluctuation can cause them to crack. The phenomenon is more intense for objects without atmospheres, such as asteroids, where temperatures vary wildly. Therefore, even though the Trojans are farther from the Sun than rocks on Earth, they’ll likely show more signs of thermal fracturing.
Solar Wind-Swept

Like everything in our solar system, asteroids are battered by the solar wind, a steady stream of particles, magnetic fields, and radiation that flows from the Sun. For the most part, Earth’s magnetic field protects us from this bombardment. Without magnetic fields or atmospheres of their own, asteroids receive the brunt of the solar wind. When incoming particles strike an asteroid, they can kick some material off into space, changing the fundamental chemistry of what’s left behind.
Follow along with Lucy’s journey with NASA Solar System on Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter, and be sure to tune in for the launch at 5 a.m. EDT (09:00 UTC) on Saturday, Oct. 16 at nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

August 2021, South of France. I am proud to share my first picture of Jupiter. I have stacked frames from a 2min45s video.

Milky Way at Quairading, Western Australia
Nikon d5500 - 50mm - ISO 4000 - f/2.8 - Foreground: 21 x 20 seconds - Sky: 34 x 30 seconds - iOptron SkyTracker - Hoya Red Intensifier filter

NGC 6523, Lagoon

Heart of the Scorpion

Scorpio, Milky Way and Jupiter

